The Role of IoT in Real-Time Fleet Tracking

In the fast-paced world of logistics and transportation, efficiency and timely information are not just goals, they are necessities. This sector, serving as the backbone of global commerce, has witnessed a transformative shift with the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT stands as a beacon of innovation, redefining the very essence of fleet management.
This detailed exploration will shed light on the pivotal role IoT plays in real-time fleet tracking, offering insights into how it revolutionizes operations, enhances decision-making, and drives efficiency to new heights. From optimizing routes to ensuring timely maintenance, IoT’s integration into fleet management marks a significant leap forward, promising a future where operational excellence is not just an aspiration but a tangible reality.
As we delve deeper, we will uncover how this technology is not merely a trend but an integral component in the sophisticated tapestry of modern fleet management, paving the way for unprecedented control and efficiency.
Understanding IoT in Fleet Management
Definition and Components
At its core, the Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices capable of collecting, sending, and receiving data. These devices, which range from simple sensors to complex processors, work collaboratively to transform raw data into meaningful insights. In the realm of fleet management, IoT components typically include:
- Sensors: Deployed in vehicles to monitor various parameters like location, speed, engine temperature, fuel usage, and more.
- Connectivity: The linchpin that enables these devices to communicate with central systems, using technologies like cellular networks, Wi-Fi, and satellite communications.
- Data Processing Platforms: Systems that process and analyze the collected data, often leveraging cloud computing for scalability and efficiency.
Integration with Fleet Management Systems
Integrating IoT with fleet management systems involves a seamless blend of hardware and software. The hardware (sensors and devices) installed in vehicles captures real-time data, which is then transmitted to software platforms. These platforms not only store and manage the data but also provide interfaces for fleet managers to monitor and analyze the information. This integration results in a comprehensive view of the fleet’s operations, allowing for real-time management and strategic planning.
Benefits of IoT in Fleet Management
The integration of IoT in fleet management reaps numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced Asset Utilization: IoT enables better tracking and management of vehicles, leading to improved asset utilization and reduced downtime.
- Operational Efficiency: Real-time data helps in making informed decisions, optimizing routes, and reducing fuel consumption.
- Safety and Compliance: Improved monitoring of vehicles and drivers enhances safety and ensures compliance with regulatory standards.
- Cost Savings: Efficient operations and predictive maintenance lead to significant cost savings in the long run.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Access to detailed analytics empowers managers to make well-informed decisions that can positively impact the bottom line.
Real-Time Tracking and Monitoring
![]()
GPS Tracking and Route Optimization
One of the most critical functions of IoT in fleet management is GPS tracking. This feature allows for precise, real-time location tracking of each vehicle in the fleet. The data collected through GPS tracking is instrumental in:
- Dynamic Route Optimization: IoT systems analyze traffic patterns, weather conditions, and road work to suggest the most efficient routes, reducing travel time and fuel costs.
- Enhanced Delivery Schedules: Accurate GPS tracking helps in creating more reliable and efficient delivery schedules, improving overall customer satisfaction.
Driver Behavior Monitoring
Beyond vehicle location, IoT devices are pivotal in monitoring driver behavior. This aspect of fleet management focuses on:
- Safety: By tracking behaviors such as speeding, harsh braking, and rapid acceleration, fleet managers can identify risky driving habits and implement targeted training programs to enhance safety.
- Efficiency: Understanding driving patterns helps in optimizing fuel usage and reducing wear and tear on vehicles.
Immediate Response Capabilities
Real-time tracking isn’t just about knowing where your vehicles are; it’s about being able to respond promptly to any situation. This capability is crucial for:
- Dealing with Emergencies: Quick response to vehicle breakdowns or accidents, ensuring driver safety and minimizing downtime.
- Adapting to Changes: Whether it’s rerouting due to traffic congestion or responding to customer requests, real-time data allows fleet managers to be more agile and responsive.
Predictive Maintenance
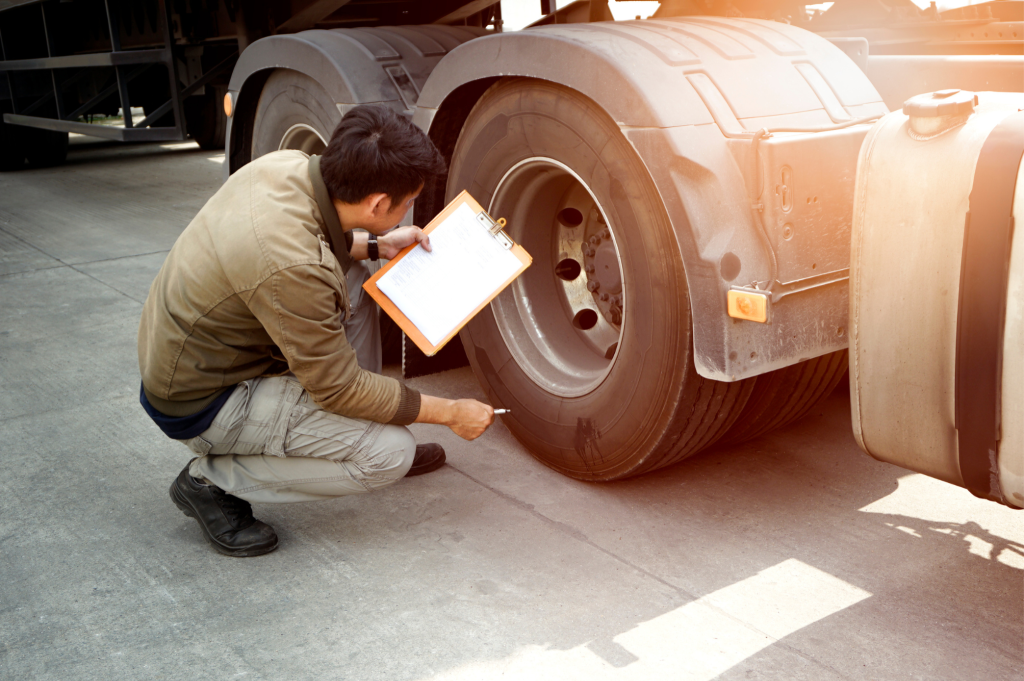

Vehicle Health Monitoring
IoT technology transforms fleet maintenance from a reactive to a proactive approach. Through continuous monitoring of vehicle health, IoT devices provide real-time diagnostics, flagging issues before they escalate into major problems. Key aspects include:
- Engine Performance: Sensors monitor engine parameters, alerting to potential issues like overheating or abnormal emissions.
- Tire Pressure and Wear: Regular monitoring ensures tires are maintained at optimal pressure, reducing wear and improving fuel efficiency.
- Battery Life and Electrical Systems: Early detection of battery or electrical issues can prevent unexpected breakdowns.
Cost Benefits of Predictive Maintenance
The shift to predictive maintenance offers several financial benefits:
- Reduced Downtime: Addressing issues before they lead to breakdowns keeps vehicles on the road longer, maintaining operational continuity.
- Extended Vehicle Lifespan: Regular maintenance based on real-time data can extend the overall lifespan of fleet vehicles.
- Lower Repair Costs: Preventative maintenance typically incurs lower costs compared to major repairs stemming from neglected issues.
Case Examples
Implementing IoT-based predictive maintenance can lead to significant improvements in fleet management. For instance, a logistics company may use IoT data to schedule maintenance during off-peak hours, ensuring maximum vehicle availability during high-demand periods. Another example could be a transportation service identifying battery issues before they cause vehicle failure, avoiding service interruptions and maintaining customer trust.
Enhancing Safety and Compliance

Safety Improvements Through IoT
One of the paramount concerns in fleet management is safety, and IoT plays a critical role in enhancing it. By providing real-time data on vehicle operation and driver behavior, IoT enables:
- Proactive Safety Measures: With data on driving patterns, companies can tailor safety training programs to address specific concerns, reducing the risk of accidents.
- Real-Time Alerts: IoT devices can alert drivers to potential safety issues, such as harsh weather conditions or vehicle malfunctions, allowing for immediate corrective action.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with transportation regulations is crucial for fleet management. This includes adherence to the Electronic Logging Devices (ELD) mandate and Hours of Service (HOS) rules. IoT devices can serve as ELDs, providing accurate driving hour logs. They also ensure maintenance records are automated, simplifying compliance with safety standards. In this context, GoFleet offers an efficient approach, blending regulatory compliance with enhanced safety. Learn more about how this is achieved through their innovative solution here.
Data Analytics: From Data to Decision Making

Data Analysis and Insights
The vast amount of data collected by IoT devices is a goldmine of insights. However, the true value lies in processing this data to inform decision-making:
- Operational Insights: Analyzing data trends can reveal insights into fleet performance, identifying areas for improvement.
- Customized Reports: IoT platforms can generate tailored reports, providing fleet managers with the information they need to make informed decisions.
Influencing Operational Decisions
The actionable insights derived from IoT data can significantly influence operational decisions:
- Fleet Optimization: Data-driven insights can inform decisions on fleet expansion, vehicle replacement, or route adjustments.
- Cost Management: Understanding patterns in fuel usage, maintenance costs, and driver efficiency can lead to more effective cost management strategies.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Addressing Challenges in IoT Implementation
While IoT brings transformative benefits to fleet tracking, it also presents certain challenges that need addressing:
- Data Security and Privacy: With the increased flow of data, ensuring its security and safeguarding privacy becomes crucial. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is essential.
- Cost of Implementation: The initial investment in IoT technology can be significant. However, the long-term ROI in terms of efficiency and cost savings often justifies the expenditure.
- Technology Integration: Integrating IoT with existing systems can be complex. It requires careful planning and potentially specialized IT support.
The Future of IoT in Fleet Tracking
Looking ahead, the potential of IoT in fleet management is boundless. Future advancements may include:
- Advanced Data Analytics and Machine Learning: Leveraging machine learning algorithms for deeper insights and predictive analytics.
- Increased Automation: IoT could pave the way for more automated processes, including potentially autonomous vehicles in fleets.
- Enhanced Connectivity: As 5G and other advanced communication technologies evolve, they will further enhance the capabilities of IoT in fleet management.
Conclusion

The integration of IoT in real-time fleet tracking is not just an upgrade; it’s a revolution in fleet management. This technology brings a new level of efficiency, safety, and insight, transforming how fleets operate and compete in the fast-paced world of logistics and transportation. As we have seen, the benefits of IoT in fleet tracking are extensive, from enhanced route optimization to proactive maintenance and improved safety. However, embracing this technology also requires navigating its challenges, particularly in terms of implementation and data security.


![Putlocker Proxy | Putlocker online Alternatives Sites [100% Working] Updated List](https://technonguide.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/putlocker-800x450.jpg)