Data in the contemporary world is continually evolving, and data transit between firms is changing as well. When data had to be transported across several platforms in the past, the records of the transactions between the platforms were kept in the form of papers. Because these documents could be readily modified or updated, a new technique known as EDI Mapping was created to address the shortcomings of the old document approach.
What is EDI Mapping?
EDI Mapping is the process of converting EDI data into forms that are easier to comprehend in a technological setting. During the Mapping event, all data structures are transformed into EDI standard formats such as EDIFACT and ANSI X12.
In an EDI Mapping process, data in one format is initially acquired from one ERP system, and then the message standard is chosen and transferred to the other ERP system once the link has been created.
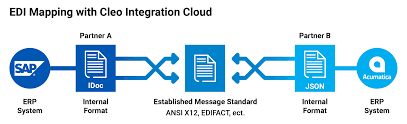
The following diagram depicts the procedure –
The SAP ERP system on the left uses an internal format called IDoc. It transforms the IDoc file into an EDI transaction and delivers it to the trade partner using a defined EDI standard, such as ANSI X12 or EDIFACT.
Because the trading partner’s ERP (Acumatica) utilises JSON as its internal format, the EDI file is converted to a JSON file before being ingested into Acumatica ERP on the righthand side.
EDI system mapping is bidirectional, which means that it isn’t limited to a left-to-right flow, dataflows in both ways
Advantages of EDI Mapping
EDI mapping provides a complete solution that unifies several supply chain partners into a single system. The following are some of the most significant benefits that this provides:
- Automation: EDI mapping automatically communicates external data to critical internal systems. The procedure is reproducible and does not require any human interaction. Aside from considerably simplifying what may be a complex procedure, this removes human errors, which are responsible for over 90% of data breaches and significantly delay operations.
- Connection: A link or simplified communication is one of the most crucial mapping benefits. The ability to effectively share data across even huge supply chains using flat-file formats is especially useful since it eliminates the need for same-language integrations. This advantage also enables effective integrations with supply chain partners that are wholly unfamiliar with, or ill-equipped for, EDI in general, when it comes to EDI-to-other mapping approaches.
- Affordability: With customized technologies that adapt to changing supply chain mapping methods and eliminate the need for human input, EDI mapping has the potential to substantially decrease costs.
Steps involved in EDI Process
There are mainly 3 steps involved in the EDI Process –
Step 1: Document Preparation– The preparation of the documents that will be sent is the initial stage in any EDI procedure. To develop all of the essential electronic documents, the data must be collected and structured. You can determine whether these require human input, electronically reformatted data, or data outputs from your system.
Depending on the scope of your operation, you may either do the preparation manually or buy software with EDI file capabilities built-in. The documents are now ready for translation after they have been prepared.
Step 2: Document translation into EDI format– The acquired electronic data must then be sent via a data translator programme to be converted into an EDI standard format. There are a number of software choices available on the market for translating segments and data items. This is where the real EDI mapping takes place, and the internal data is matched up with the EDI data. If you want them to manage the translation process, EDI service providers frequently provide translation services that may be utilized for this purpose as well.
Step 3: Connection and transmission of EDI documents- Once all essential papers have been translated, they are ready to be sent to your business partners and other important parties through a secure link. To do so, you must first choose how the link will be made. You can connect directly using AS2, connect to an EDI network provider, or utilize another secure internet protocol. You may even build a secure connection using a mix of protocols before sending EDI documents to your partners and other parties involved.
How to implement EDI Mapping
- Ensure elements of organizational structure: The first thing to check is if all of the requirements are available. It is critical to have an adequate organizational structure that includes an EDI coordinator, a steering committee, a senior management sponsor, and a dedicated EDI team. All of these will be critical to the system’s internal and external implementation functions.
- Review functional areas strategically: The functional regions of EDI deployment are the next aspect to investigate. Examine what your EDI system can perform in terms of your requirements. Examine if data redundancy has been removed, redundant business cycle stages have been eliminated, manual work has been greatly reduced, and whether customer service has improved as a result of the EDI system in place.
- Survey and analyze cost & efficiency: It’s also critical that the EDI system in issue be both cost-effective and efficient in meeting the transactional needs of customers, suppliers, and trade partners. “Cost Benefits Analysis” may be performed to examine the same. An EDI survey will assist you to evaluate the present system’s strengths and shortcomings, as well as any remaining data integration requirements according to the implementation timetable. This guarantees that suitable data linkages are in place for EDI Mapping.
- Select an EDI solution that is Business focused: The next step is to select an EDI solution that best matches your company’s needs. This ensures that EDI Mapping is well-integrated with the company’s business ideologies and does not consume additional company resources or complicate the process.
- Choose the apt EDI network provider: This is usually reserved for major corporations and those that deal with a high number of transactions. An EDI Network Provider may be a terrific way to quickly translate and handle business and financial documents, and some providers can even assist with internal EDI mapping. As a result, selecting an appropriate EDI Network Provider is critical.
- Integrate EDI with your business: The next stage will be to seamlessly integrate the EDI system into the business operations. The ideal approach to achieve this is to meet all client needs and integrate all essential internal systems that need to communicate data, all while keeping in mind the projected workload.
- Initiate data integration across your business: Data integration can begin when the basic procedures have been successfully set up. In order to properly translate the data sets involved, all data from internal and external systems must be confirmed. This is the initial step in establishing a comprehensive EDI Mapping strategy.
- Implement data mapping across the business: The next and most important phase in EDI Mapping is to connect data and ensure a smooth flow of information between internal systems and traders. This is necessary for effective and accurate data mapping, as well as a seamless procedure.
- Identify a pilot project: Before you start using the EDI system across the business community, you need to choose a trial project. This is because a pilot project effectively tests the system with a small group of partners to ensure that all of the components are working properly.
- Extend EDI to trading partners: The EDI implementation is complete after it has been examined, established, and tested, and it is ready to be extended to trading partners. The system configuration may be modified and fine-tuned as your company objectives and requirements change. This guarantees that the EDI Mapping is accurate.
EDI Mapping for Modern Businesses
Aside from the financial benefits, the most significant benefit is an improvement in overall productivity and efficiency. You may decrease your business cycle time by up to 65% with EDI. By adopting an automated internal system, transactions between organisations may be done in a flash. Common paperwork and orders are processed automatically, with supply chain tracking in real-time and no lag caused by human entry.
By removing the need for regular human interaction, you may save money on labour costs associated with processing corporate documents. Your employees will be able to engage on higher-value tasks, resulting in a more skilled workforce.
Conclusion
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) mapping has proven to be an effective technique for businesses because it allows you to automate your business transactions while also adding an element of accuracy and robust connection functions, and business invoicing and transactional communications with partners can be easily streamlined.
EDI software solutions make such transactions much easier across a variety of platforms. As a result, numerous retail, manufacturing, pharmaceutical, and automotive organizations have established themselves as important EDI clients, utilizing Electronic Data Interchange daily.


